# Declaring Items
Items are declared using a simple class definition syntax and Field objects. Here is an example:
import scrapy | |
class Product(scrapy.Item): | |
name = scrapy.Field() | |
price = scrapy.Field() | |
stock = scrapy.Field() | |
tags = scrapy.Field() | |
last_updated = scrapy.Field(serializer=str) |
注
Those familiar with Django will notice that Scrapy Items are declared similar to Django Models, except that Scrapy Items are much simpler as there is no concept of different field types.
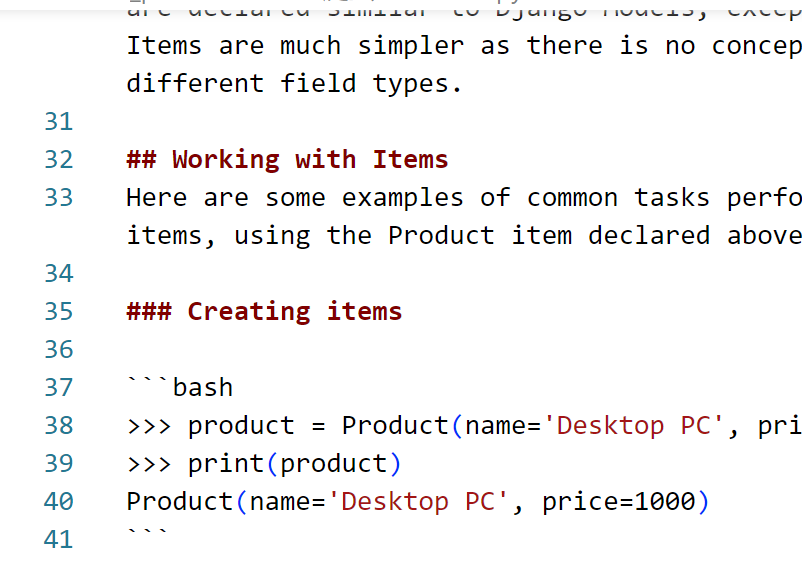
# Working with Items
Here are some examples of common tasks performed with items, using the Product item declared above.
# Creating items
>>> product = Product(name='Desktop PC', price=1000) | |
>>> print(product) | |
Product(name='Desktop PC', price=1000) |