# 剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格

class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == ' ') {
//s[i] = '$';
string temp = "%20";
s.replace(i, 1, temp);
i += temp.length() - 1;
}
}
return s;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int count = 0, len = s.size();
// 统计空格数量
for (char c : s) {
if (c == ' ') count++;
}
// 修改 s 长度
s.resize(len + 2 * count);
// 倒序遍历修改
for(int i = len - 1, j = s.size() - 1; i < j; i--, j--) {
if (s[i] != ' ')
s[j] = s[i];
else {
s[j - 2] = '%';
s[j - 1] = '2';
s[j] = '0';
j -= 2;
}
}
return s;
}
};

# 剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表

class Solution { | |
public: | |
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { | |
ListNode* ptr = head; | |
vector<int> ve; | |
while (ptr != NULL) { | |
ve.push_back(ptr->val); | |
ptr = ptr->next; | |
} | |
reverse(ve.begin(), ve.end()); | |
return ve; | |
} | |
}; |
使用 algorithm 头文件中的 reverse 函数,

class Solution { | |
public: | |
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { | |
recur(head); | |
return res; | |
} | |
private: | |
vector<int> res; | |
void recur(ListNode* head) { | |
if(head == nullptr) return; | |
recur(head->next); | |
res.push_back(head->val); | |
} | |
}; |

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
stack<int> stk;
while(head != nullptr) {
stk.push(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
vector<int> res;
while(!stk.empty()) {
res.push_back(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
# 剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
class CQueue { | |
public: | |
CQueue() { | |
} | |
void appendTail(int value) { | |
one.push(value); | |
} | |
int deleteHead() { | |
if (one.empty()) { | |
return -1; | |
} | |
else { | |
while (!one.empty()) { | |
two.push(one.top()); | |
one.pop(); | |
} | |
int res = two.top(); | |
two.pop(); | |
while (!two.empty()) { | |
one.push(two.top()); | |
two.pop(); | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
} | |
private: | |
stack<int> one, two; | |
}; | |
/** | |
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: | |
* CQueue* obj = new CQueue(); | |
* obj->appendTail(value); | |
* int param_2 = obj->deleteHead(); | |
*/ |
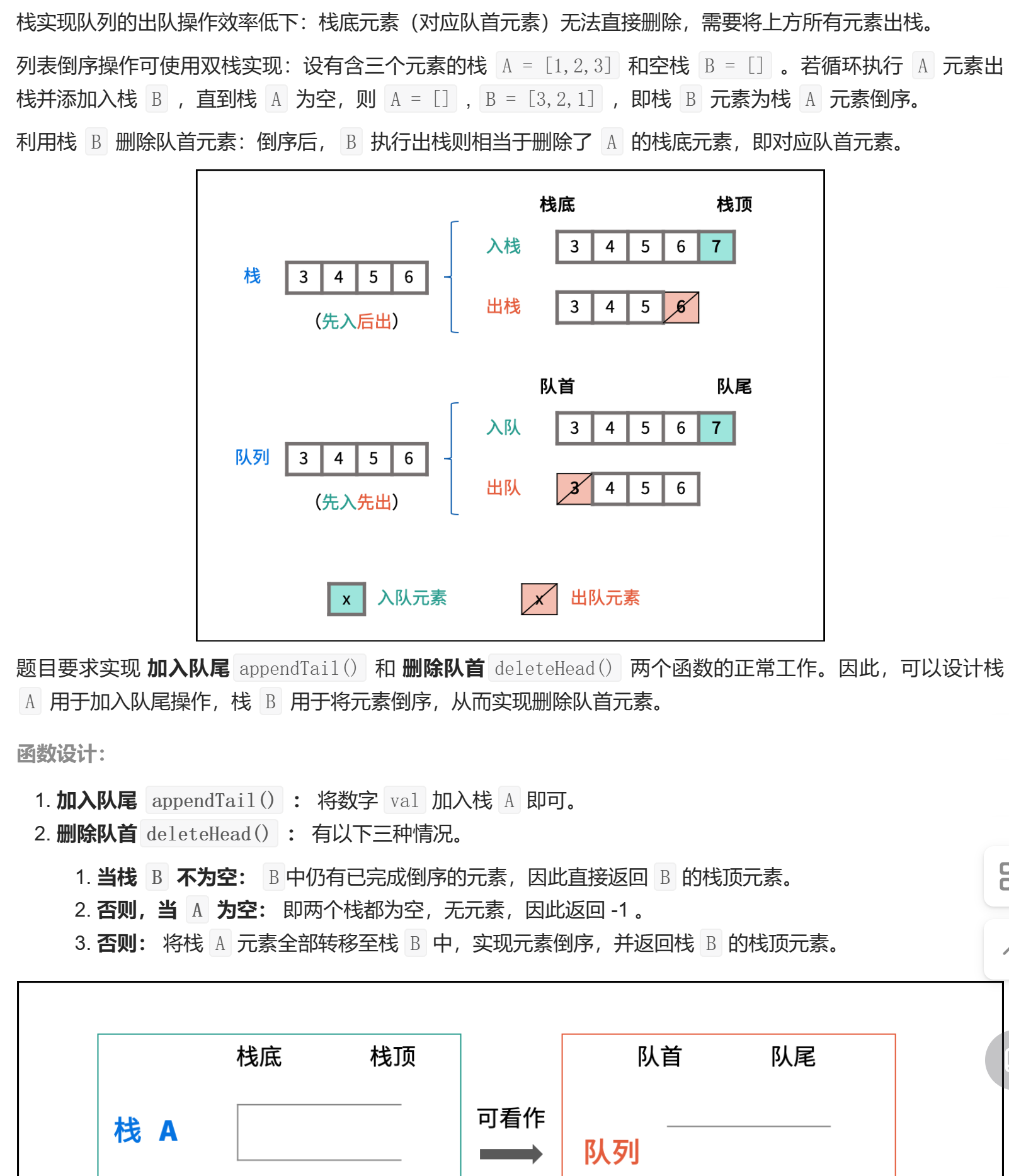

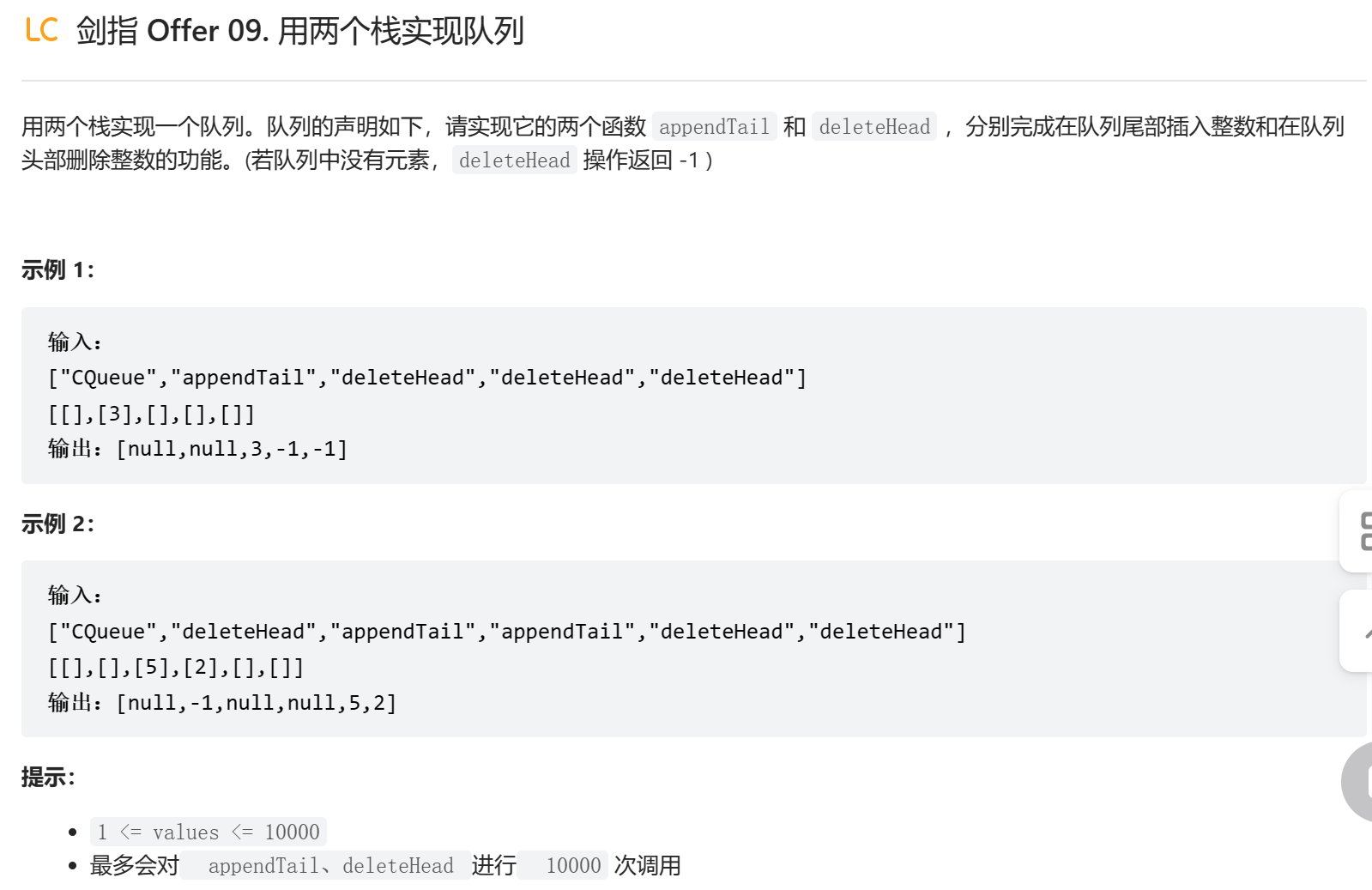
下面的做法相比上面的做法就有所优化了,考虑到可能出现连续进行的两次出队操作,所以先判断栈 B 是否为空,如果不为空就直接出栈即可。
栈 A 和栈 B 可以不同时为空。
class CQueue { | |
public: | |
stack<int> A, B; | |
CQueue() {} | |
void appendTail(int value) { | |
A.push(value); | |
} | |
int deleteHead() { | |
if(!B.empty()) { | |
int tmp = B.top(); | |
B.pop(); | |
return tmp; | |
} | |
if(A.empty()) return -1; | |
while(!A.empty()) { | |
int tmp = A.top(); | |
A.pop(); | |
B.push(tmp); | |
} | |
int tmp = B.top(); | |
B.pop(); | |
return tmp; | |
} | |
}; |
# 剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表

/** | |
* Definition for singly-linked list. | |
* struct ListNode { | |
* int val; | |
* ListNode *next; | |
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} | |
* }; | |
*/ | |
class Solution { | |
public: | |
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { | |
vector<ListNode*> ve; | |
ListNode* tempPtr = head; | |
while (tempPtr != NULL) { | |
ve.push_back(tempPtr); | |
tempPtr = tempPtr->next; | |
} | |
for (int i = ve.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) { | |
ve[i]->next = ve[i - 1]; | |
} | |
if (!ve.empty()) { | |
ve[0]->next = NULL; | |
} | |
if (!ve.empty()) { | |
return ve[ve.size() - 1]; | |
} | |
else { | |
return NULL; | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
上面是先顺序存储所有节点的指针,然后再对节点进行修改。
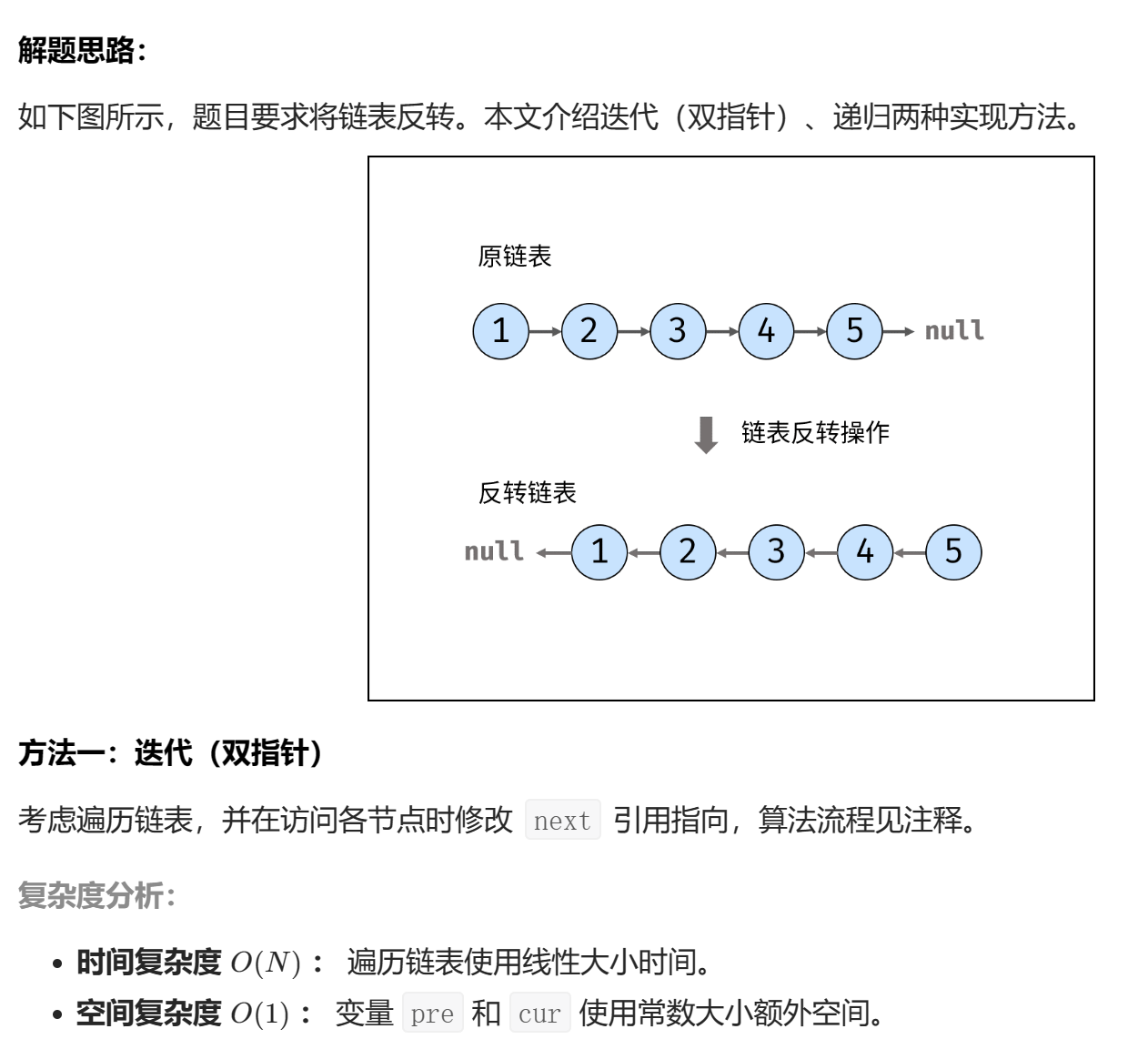
class Solution { | |
public: | |
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { | |
ListNode *cur = head, *pre = nullptr; | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
ListNode* tmp = cur->next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next | |
cur->next = pre; // 修改 next 引用指向 | |
pre = cur; //pre 暂存 cur | |
cur = tmp; //cur 访问下一节点 | |
} | |
return pre; | |
} | |
}; |

因为需要在回溯时修改各节点的 next 引用指向。因此递归函数的传入参数需要当前结点指针和上一个结点的指针。
class Solution { | |
public: | |
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { | |
return recur(head, nullptr); // 调用递归并返回 | |
} | |
private: | |
ListNode* recur(ListNode* cur, ListNode* pre) { | |
if (cur == nullptr) return pre; // 终止条件 | |
ListNode* res = recur(cur->next, cur); // 递归后继节点 | |
cur->next = pre; // 修改节点引用指向 | |
return res; // 返回反转链表的头节点 | |
} | |
}; |
这个递归函数,每一层返回的都是尾结点的指针,将此指针值自顶向下传递。
# 剑指 Offer 30. 包含 min 函数的栈

class MinStack { | |
public: | |
/** initialize your data structure here. */ | |
MinStack() { | |
} | |
void push(int x) { | |
sk.push(x); | |
if (min_sk.empty()) { | |
min_sk.push(x); | |
} | |
else { | |
int val = min_sk.top(); | |
if (x <= val) { | |
min_sk.push(x); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
void pop() { | |
int val = sk.top(); | |
sk.pop(); | |
if (val == min_sk.top()) { | |
min_sk.pop(); | |
} | |
} | |
int top() { | |
return sk.top(); | |
} | |
int min() { | |
return min_sk.top(); | |
} | |
private: | |
stack<int> sk, min_sk; | |
}; | |
/** | |
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such: | |
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack(); | |
* obj->push(x); | |
* obj->pop(); | |
* int param_3 = obj->top(); | |
* int param_4 = obj->min(); | |
*/ |

class MinStack { | |
public: | |
stack<int> A, B; | |
MinStack() {} | |
void push(int x) { | |
A.push(x); | |
if(B.empty() || B.top() >= x) | |
B.push(x); | |
} | |
void pop() { | |
if(A.top() == B.top()) | |
B.pop(); | |
A.pop(); | |
} | |
int top() { | |
return A.top(); | |
} | |
int min() { | |
return B.top(); | |
} | |
}; |
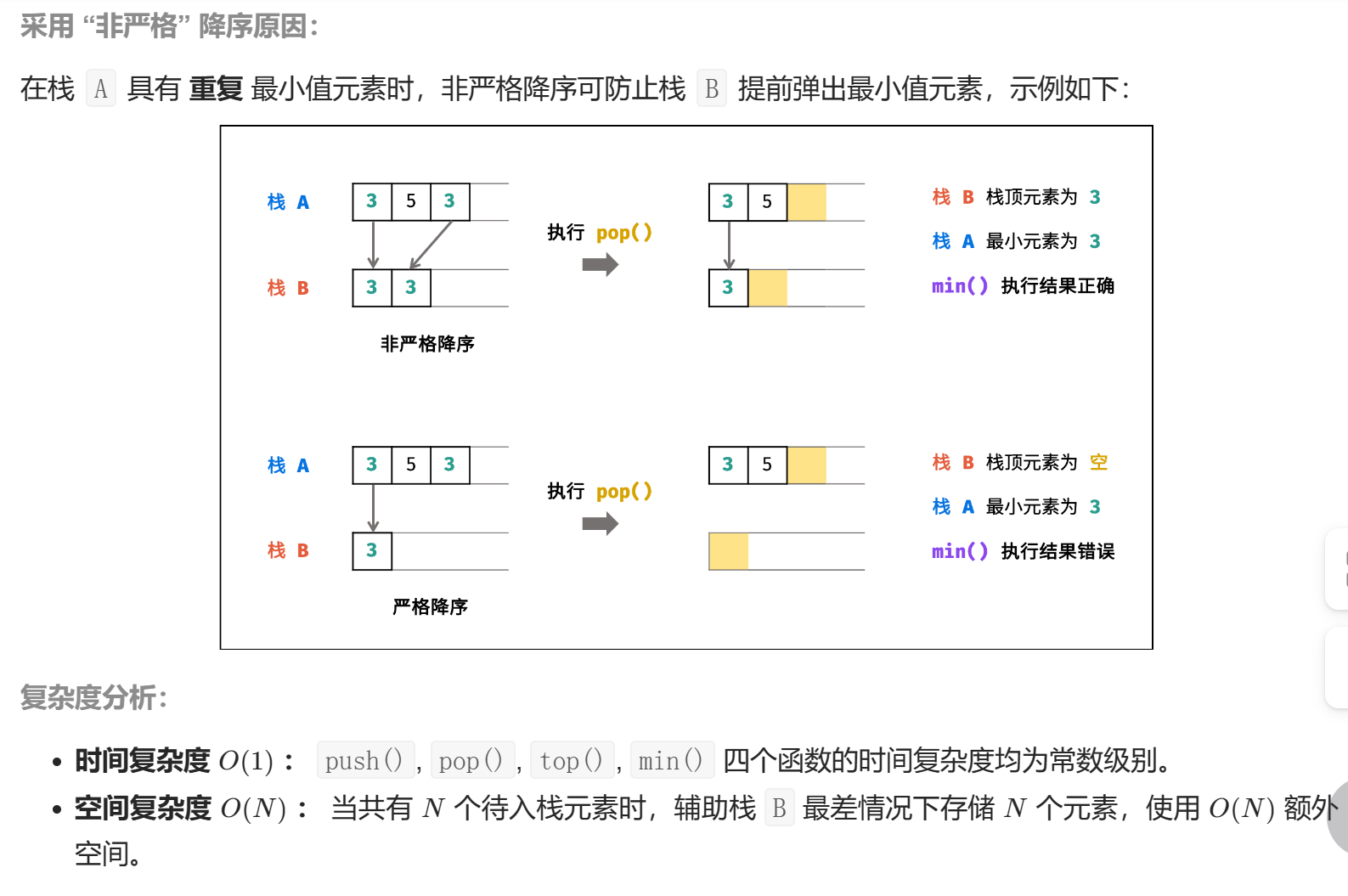
说明一下为什么出栈的时候只需要判断出栈的元素值是否和最小栈的栈顶元素就决定最小栈是否也需要出栈?
- a [i] 先于 a [i+1] 入栈
- a [i] > a [i+1] 时:a [i] 和 a [i+1] 都在栈中,出栈判断自然成
- a [i] < a [i+1] 时:a [i+1] 不会进入最小栈。
# 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
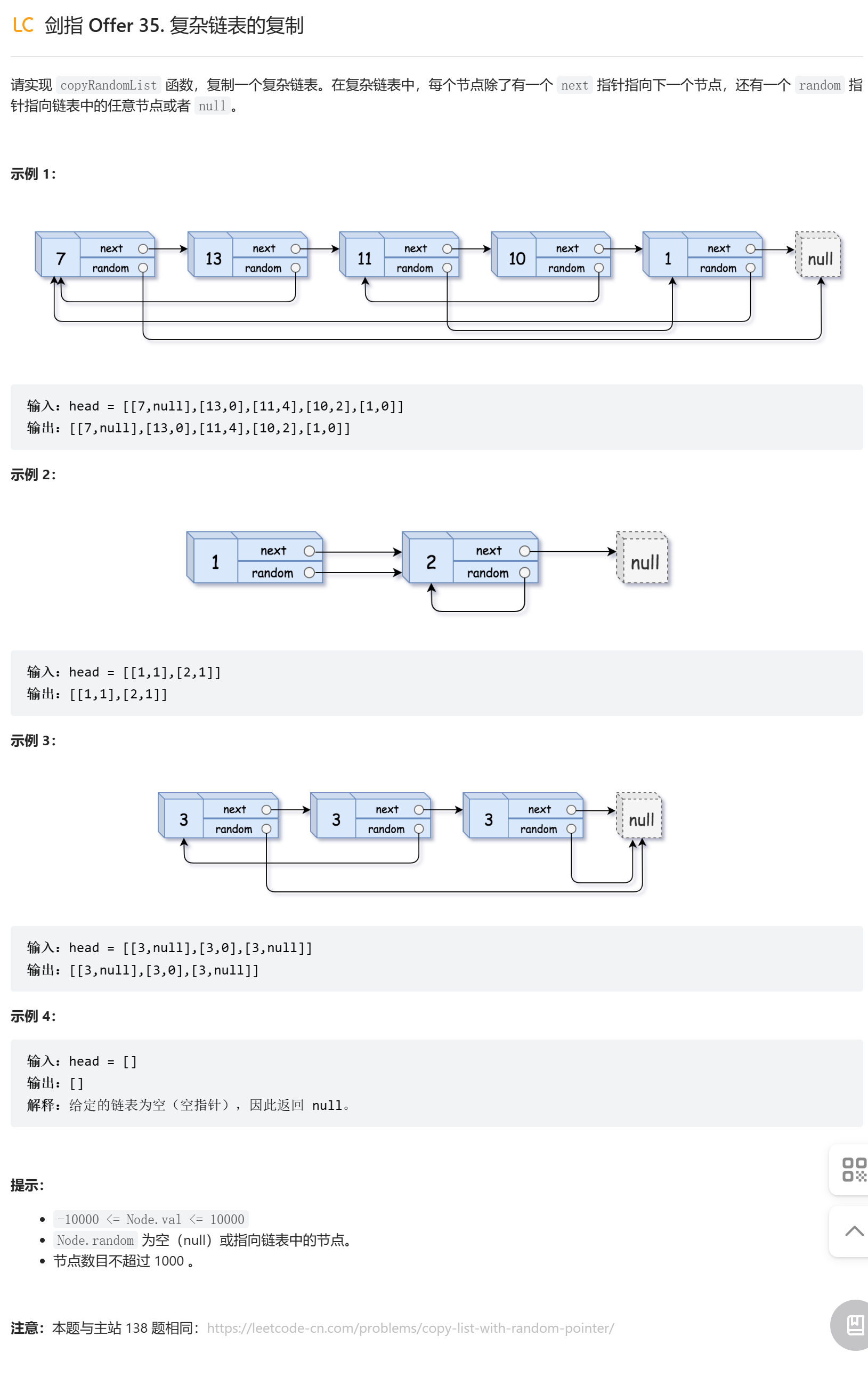
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
解题思路:
普通链表的节点定义如下:
// Definition for a Node. | |
class Node { | |
public: | |
int val; | |
Node* next; | |
Node(int _val) { | |
val = _val; | |
next = NULL; | |
} | |
}; |
本题链表的节点定义如下:
// Definition for a Node. | |
class Node { | |
public: | |
int val; | |
Node* next; | |
Node* random; | |
Node(int _val) { | |
val = _val; | |
next = NULL; | |
random = NULL; | |
} | |
}; |
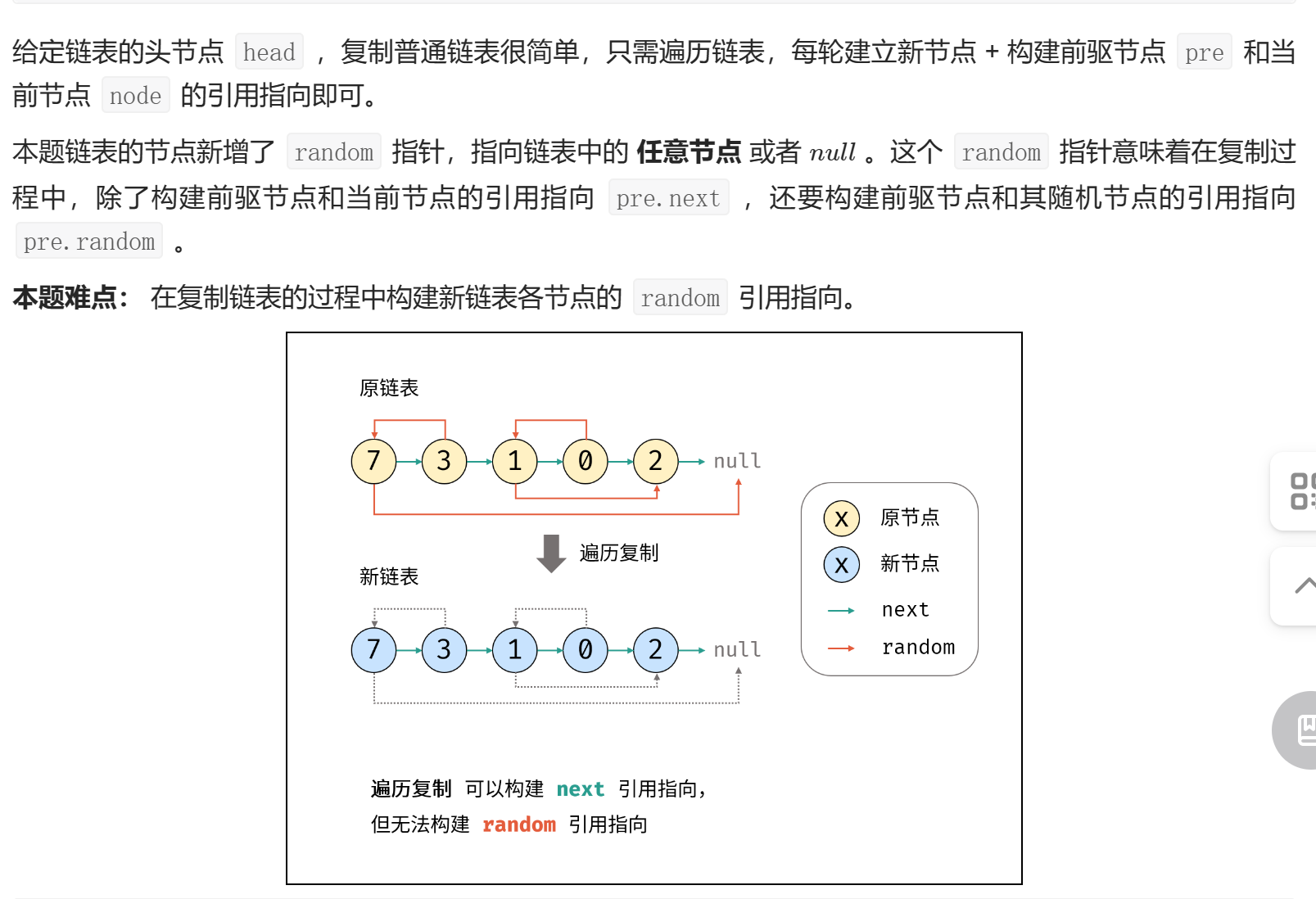
class Solution { | |
public: | |
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { | |
Node* cur = head; | |
Node* dum = new Node(0), *pre = dum; | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
Node* node = new Node(cur->val); // 复制节点 cur | |
pre->next = node; // 新链表的 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 | |
//pre->random = "???"; // 新链表的 「 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 」 无法确定 | |
cur = cur->next; // 遍历下一节点 | |
pre = node; // 保存当前新节点 | |
} | |
return dum->next; | |
} | |
}; |
上面的代码中使用了头结点法。
# 剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
class Solution { | |
public: | |
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { | |
vector<int> res; | |
int curMax; | |
curMax = nums[0]; | |
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) { | |
curMax = max(curMax, nums[i]); | |
} | |
res.push_back(curMax); | |
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) { | |
if (nums[i] >= curMax) { | |
curMax = nums[i]; | |
} | |
else if (nums[i - k] == curMax) { | |
curMax = nums[i - k + 1]; | |
for(int j = i - k + 2; j <= i; j++){ | |
curMax = max(curMax, nums[j]); | |
} | |
} | |
res.push_back(curMax); | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
}; |
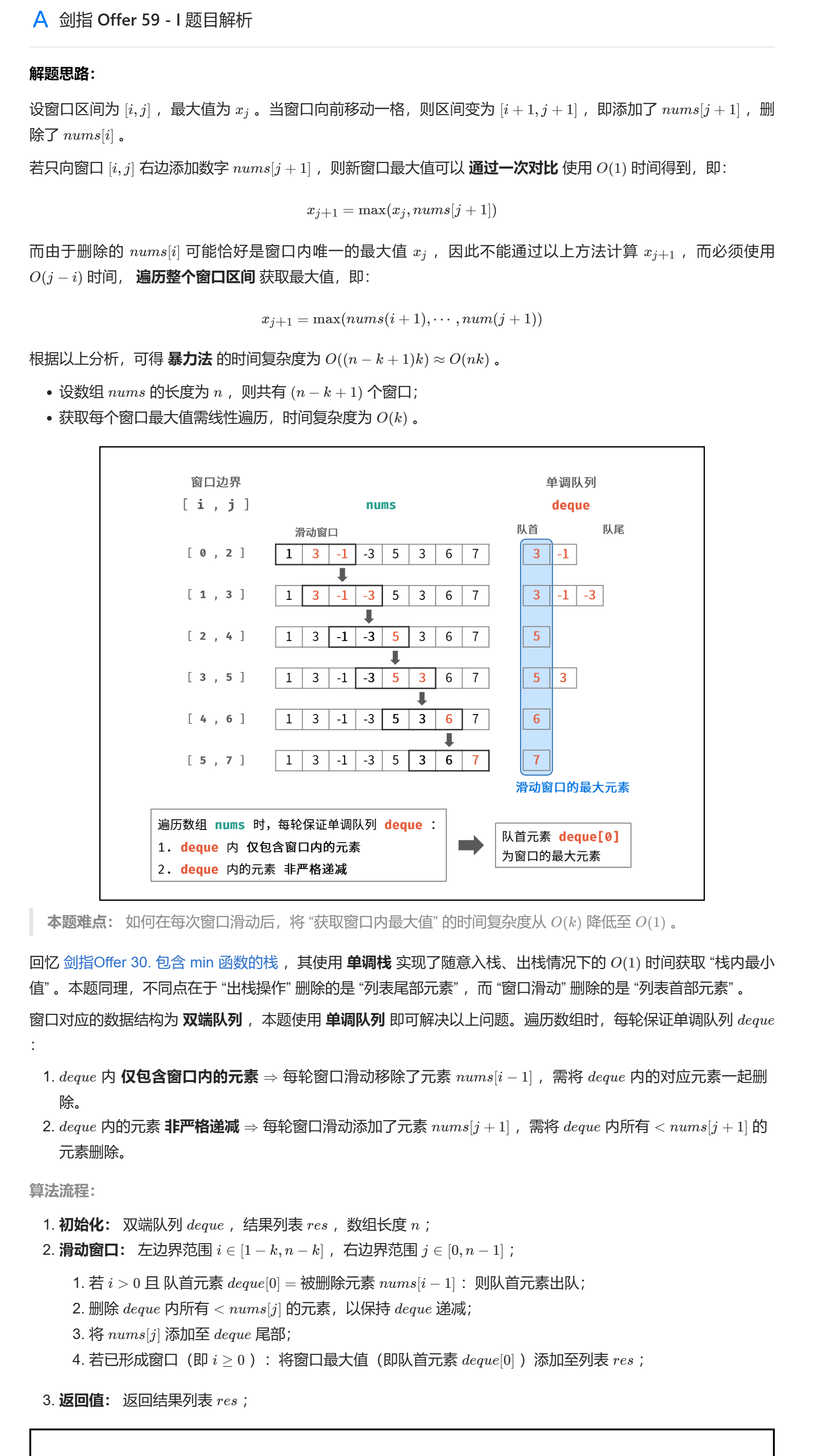
上面的暴力解法会超时。
class Solution { | |
public: | |
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { | |
vector<int> res; | |
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { | |
myDqIn(nums[i]); | |
} | |
res.push_back(this->dq.front()); | |
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) { | |
myDqIn(nums[i]); | |
myDqOut(nums[i - k]); | |
res.push_back(this->dq.front()); | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
private: | |
deque<int> dq; | |
void myDqIn(int val) { | |
if (this->dq.empty()) { | |
this->dq.push_back(val); | |
} | |
else { | |
while (!this->dq.empty() && this->dq.back() < val) { | |
this->dq.pop_back(); | |
} | |
this->dq.push_back(val); | |
} | |
} | |
void myDqOut(int val) { | |
if (val == this->dq.front()) { | |
this->dq.pop_front(); | |
} | |
} | |
}; |
说明一下出队列时为什么只需要判断该值是否和队首元素相同?
- a [i] > a [i+1] 时:两者均在队列中,a [i] 出队判断自然成立
- a [i] < a [i+1] 时:a [i+1] 入队后会将 a [i] 出队,即 a [i] 不在队列中了。所以出队的时候,如果 a [i] 比队首元素小,说明 a [i] 之后入队的有比 a [i] 更大的元素,此元素入队时把 a [i] 给搞出去了。
注意非严格递减,因为可能窗口内有两个相同的元素,一个出队之后,还得有一个留在队列中,否则最大值就可能出错了。
# 剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
class MaxQueue { | |
public: | |
MaxQueue() { | |
} | |
int max_value() { | |
if (dq.empty()) | |
return -1; | |
else | |
return dq.front(); | |
} | |
void push_back(int value) { | |
if (q.empty()) { | |
q.push(value); | |
dq.push_back(value); | |
} | |
else { | |
q.push(value); | |
while (!dq.empty() && dq.back() < value) { | |
dq.pop_back(); | |
} | |
dq.push_back(value); | |
} | |
} | |
int pop_front() { | |
if (q.empty()) | |
return -1; | |
int val = q.front(); | |
q.pop(); | |
if (val == dq.front()) { | |
dq.pop_front(); | |
} | |
return val; | |
} | |
private: | |
queue<int> q; | |
deque<int> dq; | |
}; | |
/** | |
* Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: | |
* MaxQueue* obj = new MaxQueue(); | |
* int param_1 = obj->max_value(); | |
* obj->push_back(value); | |
* int param_3 = obj->pop_front(); | |
*/ |

class MaxQueue { | |
queue<int> que; | |
deque<int> deq; | |
public: | |
MaxQueue() { } | |
int max_value() { | |
return deq.empty() ? -1 : deq.front(); | |
} | |
void push_back(int value) { | |
que.push(value); | |
while(!deq.empty() && deq.back() < value) | |
deq.pop_back(); | |
deq.push_back(value); | |
} | |
int pop_front() { | |
if(que.empty()) return -1; | |
int val = que.front(); | |
if(val == deq.front()) | |
deq.pop_front(); | |
que.pop(); | |
return val; | |
} | |
}; |
# 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
/* | |
// Definition for a Node. | |
class Node { | |
public: | |
int val; | |
Node* next; | |
Node* random; | |
Node(int _val) { | |
val = _val; | |
next = NULL; | |
random = NULL; | |
} | |
}; | |
*/ | |
class Solution { | |
public: | |
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { | |
if (head == NULL) | |
return NULL; | |
Node* temp = new Node(0); | |
map<Node*, Node*> mp; // 旧节点的指针到新节点的指针的映射 | |
Node* p1 = head, *p2 = temp; | |
while (p1 != NULL) { | |
int val = p1->val; | |
p2->next = new Node(val); | |
p2 = p2->next; | |
mp[p1] = p2; | |
p1 = p1->next; | |
} | |
p1 = head, p2 = temp->next; | |
while (p1 != NULL) { | |
p2->random = p1->random == NULL ? NULL : mp[p1->random]; | |
p1 = p1->next; | |
p2 = p2->next; | |
} | |
return temp->next; | |
} | |
}; |
class Solution { | |
public: | |
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { | |
Node* cur = head; | |
Node* dum = new Node(0), *pre = dum; | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
Node* node = new Node(cur->val); // 复制节点 cur | |
pre->next = node; // 新链表的 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 | |
//pre->random = "???"; // 新链表的 「 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 」 无法确定 | |
cur = cur->next; // 遍历下一节点 | |
pre = node; // 保存当前新节点 | |
} | |
return dum->next; | |
} | |
}; |

class Solution { | |
public: | |
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { | |
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr; | |
Node* cur = head; | |
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> map; | |
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射 | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
map[cur] = new Node(cur->val); | |
cur = cur->next; | |
} | |
cur = head; | |
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向 | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
map[cur]->next = map[cur->next]; | |
map[cur]->random = map[cur->random]; | |
cur = cur->next; | |
} | |
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点 | |
return map[head]; | |
} | |
}; |
class Solution { | |
public: | |
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { | |
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr; | |
Node* cur = head; | |
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表 | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->val); | |
tmp->next = cur->next; | |
cur->next = tmp; | |
cur = tmp->next; | |
} | |
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向 | |
cur = head; | |
while(cur != nullptr) { | |
if(cur->random != nullptr) | |
cur->next->random = cur->random->next; | |
cur = cur->next->next; | |
} | |
// 3. 拆分两链表 | |
cur = head->next; | |
Node* pre = head, *res = head->next; | |
while(cur->next != nullptr) { | |
pre->next = pre->next->next; | |
cur->next = cur->next->next; | |
pre = pre->next; | |
cur = cur->next; | |
} | |
pre->next = nullptr; // 单独处理原链表尾节点 | |
return res; // 返回新链表头节点 | |
} | |
}; |